PROUCTS LIST
NEWS
超高速視頻級原子力顯微鏡—HS-AFM的詳細(xì)資料:
超高速視頻級原子力顯微鏡—HS-AFM,一種可用來研究包括絕緣體在內(nèi)的固體材料表面結(jié)構(gòu)的分析儀器。它通過檢測待測樣品表面和一個微型力敏感元件之間的極微弱的原子間相互作用力來研究物質(zhì)的表面結(jié)構(gòu)及性質(zhì)。將一對微弱力敏感的微懸臂一端固定,另一端的微小針尖接近樣品,這時它將與其相互作用,作用力將使得微懸臂發(fā)生形變或運(yùn)動狀態(tài)發(fā)生變化。掃描樣品時,利用傳感器檢測這些變化,就可獲得作用力分布信息,從而以納米級分辨率獲得表面形貌結(jié)構(gòu)信息及表面粗糙度信息。原子力顯微鏡可以測量材料物理性質(zhì)、力學(xué)性能、磁學(xué)性能、熱學(xué)性能、電學(xué)性能等方面的一些特征信息,但在掃描成像速度上一直存在局限性,太慢的掃描速度導(dǎo)致原子力顯微鏡無法捕捉到分子間的相互作用過程和一些快速的分子動態(tài)變化。

超高速視頻級原子力顯微鏡—HS-AFM由日本 Kanazawa 大學(xué) Prof. Ando 教授團(tuán)隊(duì)研發(fā),日本RIBM公司(生體分子計測研究所株式會社,Research Institute of Biomolecule Metrology Co., Ltd)商業(yè)化的產(chǎn)品,可以達(dá)到視頻級成像的商業(yè)化原子力顯微鏡。HS-AFM突破了傳統(tǒng)原子力顯微鏡“掃描成像速慢"的限制,能夠在液體環(huán)境下超快速動態(tài)成像,分辨率為納米水平。樣品無需特殊固定,不影響生物分子的活性,尤其適用于生物大分子互作動態(tài)觀測。超高速視頻級原子力顯微鏡HS-AFM主要有兩種型號,SS-NEX樣品掃描(Sample-Scanning HS-AFM)以及PS-NEX探針掃描(Probe-Scanning HS-AFM)。推出至今,已有180多位用戶,發(fā)表 SCI 文章 300 余篇,包括Science, Nature, Cell 等雜志。
2023年初1月份,北京佰司特科技有限責(zé)任公司正式簽約日本RIBM公司的超高速視頻級原子力顯微鏡(HS-AFM),成為日本RIBM公司在中國大陸地區(qū),香港,澳門,中國臺灣以及新加坡的代理商,全權(quán)負(fù)責(zé)日本RIBM公司的超高速視頻級原子力顯微鏡(HS-AFM)的市場推廣,客戶拜訪,宣傳講座,路演DEMO,銷售定價,投標(biāo)簽約,進(jìn)出口以及安裝售后等所有事宜。

相較于目前市場上的原子力顯微鏡成像設(shè)備,HS-AFM突破了 “掃描成像速慢"的限制,掃描速度高可達(dá) 20 frame/s,并且有 4 種掃描臺可供選擇。樣品無需特殊固定染色,不影響生物分子的活性,尤其適用于生物大分子互作動態(tài)觀測。液體環(huán)境下直接檢測,超快速動態(tài)成像,分辨率為納米水平。探針小,適用于生物樣品;懸臂探針共振頻率高,彈簧系數(shù)小,避免了對生物樣品等的損傷。懸臂探針可自動漂移校準(zhǔn),適用于長時間觀測。采用動態(tài)PID控制,高速掃描時仍可獲得清晰的圖像。XY軸分辨率2nm;Z軸分辨率0.5nm。
HS-AFM不僅擁有超高掃描速率與原子級別分辨率,而且具有操作的簡易性,使得對單分子動態(tài)過程的捕捉變得十分方便,為科研工作者研究和理解生物物理、生物化學(xué)、分子生物學(xué)、病毒學(xué)以及生物醫(yī)學(xué)等領(lǐng)域的單分子動態(tài)過程提供了一款強(qiáng)大的工具。
全新的HS-AFM采用了新的高頻微懸臂架構(gòu),更低噪音、更高穩(wěn)定性的控制器,高速掃描器,緩沖防震設(shè)計,主動阻尼,動態(tài)PID,驅(qū)動算法優(yōu)化,多種前沿技術(shù),可以實(shí)現(xiàn)在超高速下獲取高分辨的生物樣品信息。新系統(tǒng)整合了基于工作流程的操作軟件,直觀的用戶界面與流程化、自動化的設(shè)置使得研究人員可以專注于實(shí)驗(yàn)設(shè)計,不需要復(fù)雜的操作和條件設(shè)置,快速獲取數(shù)據(jù),加速研究的產(chǎn)出。
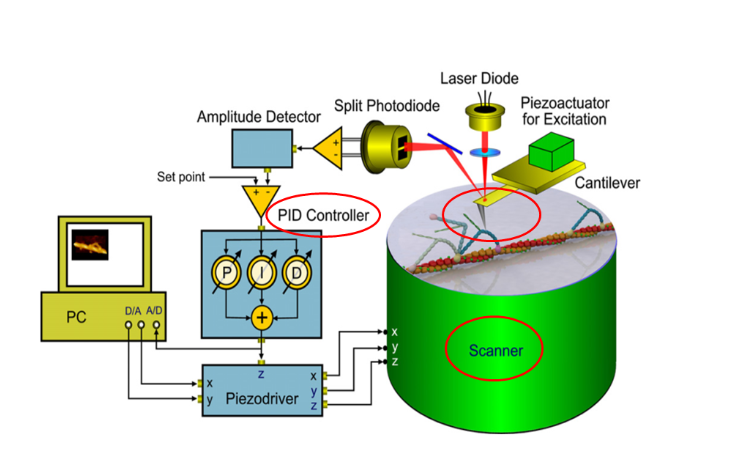
日本RIBM公司的超高速視頻級原子力顯微鏡HS-AFM的創(chuàng)新點(diǎn):
★ 高頻微懸臂
彈性系數(shù): 0.1 N/m
曲率半徑: <10 nm
共振頻率: 400-600kHz in liquid
★ 高速掃描臺
20 frames/s. (Standard scanner)
★ 緩沖防震+主動阻尼+動態(tài)PID+算法優(yōu)化
緩沖防震
主動阻尼
動態(tài)PID控制:可自動改變反饋增益,保證了HS-AFM在高速掃描條件下仍可獲得清晰的圖像
探針自動漂移校準(zhǔn),適用于長時間樣品觀測

日本RIBM公司的超高速視頻級原子力顯微鏡HS-AFM的的應(yīng)用領(lǐng)域:
從單分子到單細(xì)胞,都可直接觀測
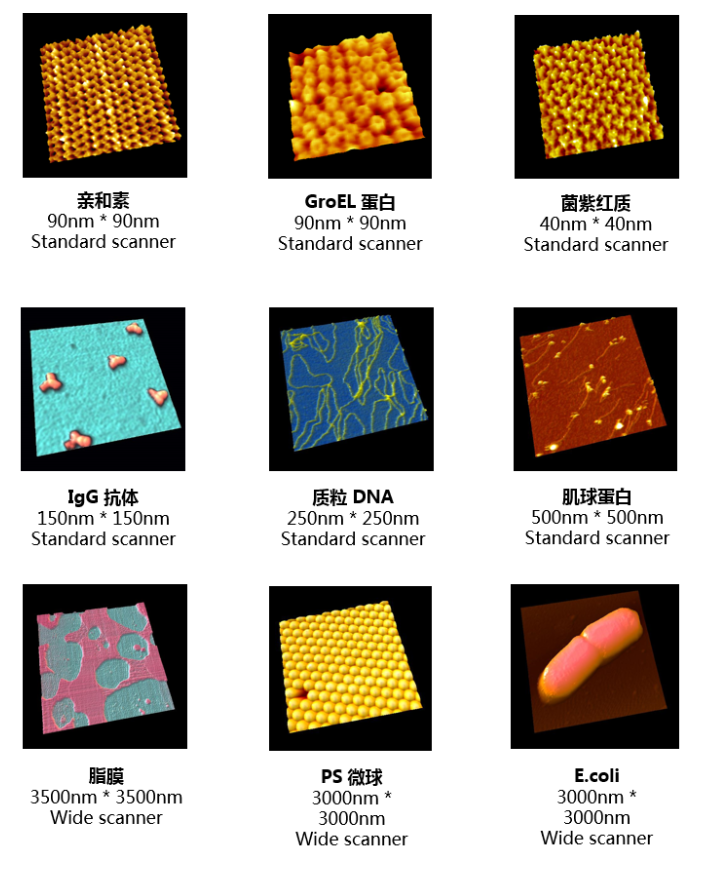
1、肌動蛋白

2、CRISPR-Cas9

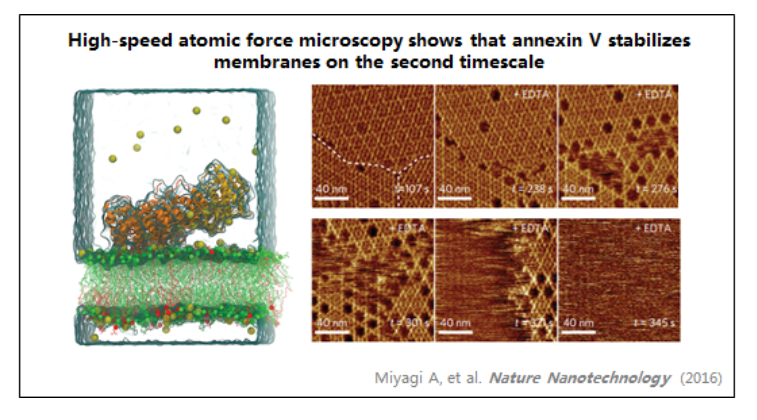
3、膜聯(lián)蛋白
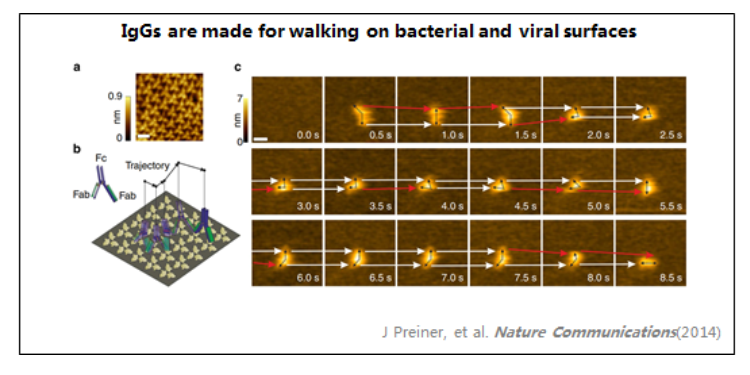
4、IgG
5、活細(xì)胞
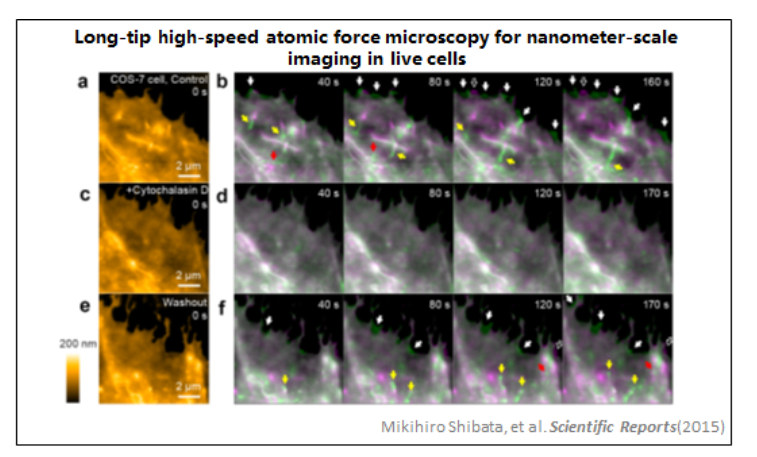
6、細(xì)菌視紫紅質(zhì)

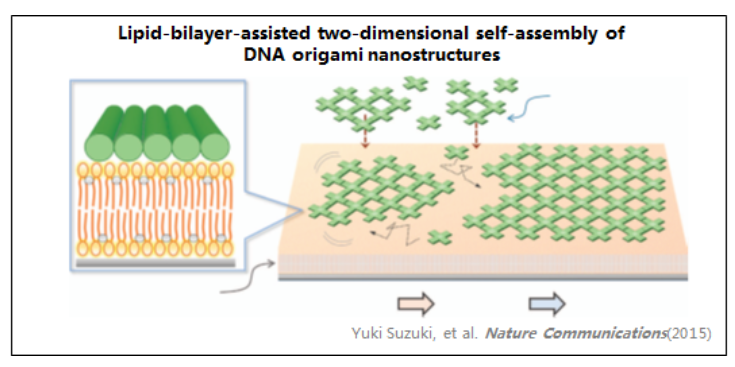
7、DNA納米結(jié)構(gòu)
8、仿生聚合物

日本RIBM公司的超高速視頻級原子力顯微鏡HS-AFM的視頻案例
1:IgG
在溶液中觀察到抗體(IgG)。
IgG呈"Y"形,兩個Fab區(qū)區(qū)分清晰。
由于錨定能力較弱,IgG保持其抗原結(jié)合能力。
2:Plasmid DNA
傳統(tǒng)AFM在沒有強(qiáng)錨定的情況下,DNA分子圖像出現(xiàn)擺動。
然而,強(qiáng)錨定可能會削弱真實(shí)的結(jié)構(gòu)和行為。
HS-AFM能清晰顯示質(zhì)粒的結(jié)構(gòu)和運(yùn)動,無強(qiáng)錨定。
3:DNA內(nèi)切酶的消化:DNase I
DNA酶I是一種隨機(jī)消化DNA的核酸內(nèi)切酶。視頻中的箭頭表示DNase I消化DNA的部分。
請參考從DNA末端消化的核酸外切酶Bal31的視頻。
4:DNA外切酶消化:Bal31
Bal31是一種從DNA鏈末端消化DNA的核酸外切酶。
視頻顯示Bal31的活性沿著DNA移動,并逐漸從DNA鏈的末端消化。
最后,DNA分子被消化,但環(huán)狀DNA未被消化。高光點(diǎn)是Bal31分子,它們與DNA的不同位置結(jié)合。
5:DNA聚合酶的DNA延伸:Phi29
雙鏈DNA(黃色)隨著時間的推移而拉長。單鏈λDNA作為模具固定在基板上。
由于從隨機(jī)六聚體引物(Red)結(jié)合到λDNA模體,phi29聚合酶(Black)以dNTP為底物合成互補(bǔ)DNA。
6:鏈親和素2D晶體中的點(diǎn)缺陷
成功地觀察到點(diǎn)缺陷在晶體中的擴(kuò)散。
從圖像上看,兩個單空位缺陷的軌跡跟蹤相對于晶格的兩個軸是明顯的各向異性的。
日本RIBM公司的超高速視頻級原子力顯微鏡HS-AFM的文獻(xiàn)列表
| Title | Journal | ||||
| Biophysical reviews top five: atomic force microscopy in biophysics | Biophysical Reviews | ||||
| Reconstruction of Three-Dimensional Conformations of Bacterial ClpB from High-Speed Atomic-Force-Microscopy Images | Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences | ||||
| A facile combinatorial approach to construct a ratiometric fluorescent sensor: application for the real-time sensing of cellular pH changes | Chemical Science | ||||
| DNA Nanotechnology to Disclose Molecular Events at the Nanoscale and Mesoscale Levels | Springer Nature | ||||
| Quantitative description of a contractile macromolecular machine | Science Advances | ||||
| Dynamic Assembly/Disassembly of Staphylococcus aureus FtsZ Visualized by High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy | International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, Vol. 22, Page 1697 | ||||
| Localization atomic force microscopy | Nature 2021 594:7863 | ||||
| Movements of mycoplasma mobile gliding machinery detected by high-speed atomic force microscopy | mBio | ||||
| An ultra-wide scanner for large-area high-speed atomic force microscopy with megapixel resolution | Scientific Reports 2021 11:1 | ||||
| A molecularly engineered, broad-spectrum anti-coronavirus lectin inhibits SARS-CoV-2 and MERS-CoV infection in vivo | Research Square | ||||
| Influenza virus ribonucleoprotein complex formation occurs in the nucleolus | bioRxiv | ||||
| Tardigrade Secretory-Abundant Heat-Soluble Protein Has a Flexible β-Barrel Structure in Solution and Keeps This Structure in Dehydration | Journal of Physical Chemistry B | ||||
| Ultrastructure of influenza virus ribonucleoprotein complexes during viral RNA synthesis | Communications Biology on | ||||
| A facile combinatorial approach to construct a ratiometric fluorescent sensor: application for the real-time sensing of cellular pH changes | Chemical Science | ||||
| Deformation of microtubules regulates translocation dynamics of kinesin | Science Advances | ||||
| Unraveling the host-selective toxic interaction of cassiicolin with lipid membranes and its cytotoxicity | bioRxiv | ||||
| Nanostructure and thermoresponsiveness of poly( N -isopropyl methacrylamide)-based hydrogel microspheres prepared via aqueous free radical precipitation polymerization | RSC Advances | ||||
| JRAB/MICAL-L2 undergoes liquid–liquid phase separation to form tubular recycling endosomes | Communications Biology 2021 4:1 | ||||
| Correlation of membrane protein conformational and functional dynamics | Nature Communications 2021 12:1 | ||||
| Non-close-packed arrangement of soft elastomer microspheres on solid substrates | RSC Advances | ||||
| Folding RNA–Protein Complex into Designed Nanostructures | Methods in Molecular Biology | ||||
| A glutamine sensor that directly activates TORC1 | Communications Biology 2021 4:1 | ||||
| Architecture of zero-latency ultrafast amplitude detector for high- speed atomic force microscopy | Applied Physics Letters | ||||
| Correlative AFM and fluorescence imaging demonstrate nanoscale membrane remodeling and ring-like and tubular structure formation by septins | Nanoscale | ||||
| Desiccation-induced fibrous condensation of CAHS protein from an anhydrobiotic tardigrade | bioRxiv | ||||
| Construction of ferritin hydrogels utilizing subunit–subunit interactions | PLOS ONE | ||||
| Monomeric α-synuclein (αS) inhibits amyloidogenesis of human prion protein (hPrP) by forming a stable αS-hPrP hetero-dimer. | Prion | ||||
| Influence of protein adsorption on aggregation in prefilled syringes | Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences | ||||
| Dynamic mechanisms of CRISPR interference by Escherichia coli CRISPR-Cas3 | bioRxiv | ||||
| An RNA Triangle with Six Ribozyme Units Can Promote a Trans- Splicing Reaction through Trimerization of Unit Ribozyme Dimers | Applied Sciences | ||||
| Faster high-speed atomic force microscopy for imaging of biomolecular processes Review of Scientific Instruments ARTICLE scitation.org/journal/rsi Faster high-speed atomic force microscopy for imaging of biomolecular processes | Rev. Sci. Instrum | ||||
| Title: Identification of lectin receptors for conserved SARS-CoV-2 glycosylation sites | bioRxiv | ||||
| Structural and dynamics analysis of intrinsically disordered proteins by high-speed atomic force microscopy | Nature Nanotechnology | ||||
| Millisecond Conformational Dynamics of Skeletal Myosin II Power Stroke Studied by High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy | ACS Nano | ||||
| High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy Reveals Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Histone Protein H2A Involution by DNA Inchworming | The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters | ||||
| Nanostructures, Thermoresponsiveness, and Assembly Mechanism of Hydrogel Microspheres during Aqueous Free-Radical Precipitation Polymerization | Langmuir | ||||
| Chained structure of dimeric F 1-like ATPase in Mycoplasma mobile gliding machinery 4 | bioRxiv | ||||
| Lipid Membrane Interaction of Peptide/DNA Complexes Designed for Gene Delivery | Langmuir | ||||
| High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy to Study Myosin Motility | Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology | ||||
| Single-molecule level dynamic observation of disassembly of the apo-ferritin cage in solution | Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics | ||||
| Atomic Force Microscopy of Biomembranes : A Tool for Studying the Dynamic Behavior of Membrane Proteins | New Techniques for Studying Biomembranes | ||||
| Adenosine leakage from perforin-burst extracellular vesicles inhibits perforin secretion by cytotoxic T-lymphocytes | PLOS ONE | ||||
| High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy Reveals the Structural Dynamics of the Amyloid-β and Amylin Aggregation Pathways | International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, Vol. 21, Page 4287 | ||||
| Molecular mechanism of the recognition of bacterially cleaved immunoglobulin by the immune regulatory receptor LILRA2 | Journal of Biological Chemistry | ||||
| Biological physics by high-speed atomic force microscopy | Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences | ||||
| Viral RNA recognition by LGP2 and MDA5, and activation of signaling through step-by-step conformational changes | Nucleic Acids Research | ||||
| Key Nucleation Stages and Associated Molecular Determinants and Processes in pH-Induced Formation of Amyloid Beta Oligomers as Revealed by High-Speed AFM | bioRxiv | ||||
| Novel Babesia bovis exported proteins that modify properties of infected red blood cells | PLoS Pathogens | ||||
| DNA origami demonstrate the unique stimulatory power of single pMHCs as T-cell antigens | Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences | ||||
| Structural insights into the mechanism of rhodopsin phosphodiesterase | Nature Communications | ||||
| Structural insights into the mechanism of rhodopsin phosphodiesterase | Nature Communications | ||||
| High-Speed AFM Reveals Molecular Dynamics of Human Influenza A Hemagglutinin and Its Interaction with Exosomes | Nano Letters | ||||
| DNA Ring Motif with Flexible Joints | Micromachines | ||||
| Nanopores: a versatile tool to study protein dynamics | Essays in Biochemistry | ||||
| Geometrical Characterization of Glass Nanopipettes with Sub-10 nm Pore Diameter by Transmission Electron Microscopy | Analytical Chemistry | ||||
| Carbon nanotube porin diffusion in mixed composition supported lipid bilayers | Scientific Reports | ||||
| One-Step Calibration of AFM in Liquid | Frontiers in Physics | ||||
| Nanoscale interaction of RecG with mobile fork DNA | Nanoscale Advances | ||||
| Convergent evolution of processivity in bacterial and fungal cellulases | Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences | ||||
| Convergent evolution of processivity in bacterial and fungal cellulases | Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America | ||||
| Interaction of the motor protein SecA and the bacterial protein translocation channel SecYEG in the absence of ATP | Nanoscale Advances | ||||
| Nanoreporter of an Enzymatic Suicide Inactivation Pathway | Nano Letters | ||||
| High-speed atomic force microscopy highlights new molecular mechanism of daptomycin action | Nature Communications | ||||
| Direct visualization of the conformational change of FUS/TLS upon binding to promoter-associated non-coding RNA | Chemical Communications | ||||
| Thermoresponsive Micellar Assembly Constructed from a Hexameric Hemoprotein Modified with Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) toward an Artificial Light-Harvesting System | Journal of the American Chemical Society | ||||
| Schizorhodopsins: A family of rhodopsins from Asgard archaea that function as light-driven inward H + pumps | Science Advances | ||||
| Two-State Exchange Dynamics in Membrane-Embedded Oligosaccharyltransferase Observed in Real-Time by High-Speed AFM | Journal of Molecular Biology | ||||
| Thermoresponsive structural changes of single poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) hydrogel microspheres under densely packed conditions on a solid substrate | Polymer Journal | ||||
| High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy Reveals Factors Affecting the Processivity of Chitinases during Interfacial Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Crystalline Chitin | ACS Catalysis | ||||
| Rad50 zinc hook functions as a constitutive dimerization module interchangeable with SMC hinge | Nature Communications | ||||
| Assembly mechanism of a supramolecular MS-ring complex to initiate bacterial flagellar biogenesis in vibrio species | Journal of Bacteriology | ||||
| Structural Dynamics of a Protein Domain Relevant to the Water- Oxidizing Complex in Photosystem II as Visualized by High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy | Journal of Physical Chemistry B | ||||
| Recent advances in bioimaging with high-speed atomic force microscopy | Biophysical Reviews | ||||
| Dynamic behavior of an artificial protein needle contacting a membrane observed by high-speed atomic force microscopy | Nanoscale | ||||
| Enhanced enzymatic activity exerted by a packed assembly of a single type of enzyme | Chemical Science | ||||
| High Speed AFM and NanoInfrared Spectroscopy Investigation of A β1–42 Peptide Variants and Their Interaction With POPC/SM/Chol/GM1 Model Membranes | Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences | ||||
| The hierarchical assembly of septins revealed by high-speed AFM | Nature Communications | ||||
| Millisecond dynamics of an unlabeled amino acid transporter | Nature Communications | ||||
| Atg9 is a lipid scramblase that mediates autophagosomal membrane expansion | Nature Structural & Molecular Biology | ||||
| A Simplified Cluster Analysis of Electron Track Structure for Estimating Complex DNA Damage Yields | International Journal of Molecular Sciences | ||||
| Supramolecular tholos-like architecture constituted by archaeal proteins without functional annotation | Scientific Reports | ||||
| Studies on the impellers generating force in muscle | Biophysical Reviews | ||||
| Diversity of physical properties of bacterial extracellular membrane vesicles revealed through atomic force microscopy phase imaging | Nanoscale | ||||
| High-Speed AFM Reveals Molecular Dynamics of Human Influenza A Hemagglutinin and Its Interaction with Exosomes | Nano Letters | ||||
| DNA density-dependent uptake of DNA origami-based two-or three- dimensional nanostructures by immune cells | Nanoscale | ||||
| Spatiotemporally tracking of nano-biofilaments inside the nuclear pore complex core | Biomaterials | ||||
| High-speed atomic force microscopy directly visualizes conformational dynamics of the HIV Vif protein in complex with three host proteins | Journal of Biological Chemistry | ||||
| Self- and Cross-Seeding on α-Synuclein Fibril Growth Kinetics and Structure Observed by High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy | ACS Nano | ||||
| Liquidity Is a Critical Determinant for Selective Autophagy of Protein Condensates | Molecular Cell | ||||
| Capturing transient antibody conformations with DNA origami epitopes | Nature Communications | ||||
| Biophysics in Kanazawa University | Biophysical Reviews | ||||
| Dynamics of oligomer and amyloid fibril formation by yeast prion Sup35 observed by high-speed atomic force microscopy | Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences | ||||
| Annexin-V stabilizes membrane defects by inducing lipid phase transition | Nature Communications | ||||
| Structure and mechanism of bactericidal mammalian perforin-2, an ancient agent of innate immunity | Science Advances | ||||
| Atomic Force Microscopy Visualizes Mobility of Photosynthetic Proteins in Grana Thylakoid Membranes | Biophysical Journal | ||||
| Construction of a Hexameric Hemoprotein Sheet and Direct Observation of Dynamic Processes of Its Formation | Chemistry Letters | ||||
| Single-molecule imaging analysis reveals the mechanism of a high- catalytic-activity mutant of chitinase A from Serratia marcescens | Journal of Biological Chemistry | ||||
| Direct observation and analysis of TET-mediated oxidation processes in a DNA origami nanochip | Nucleic Acids Research | ||||
| On-membrane dynamic interplay between anti-GM1 IgG antibodies and complement component C1q | International Journal of Molecular Sciences | ||||
| Zwitterionic Polypeptides: Chemoenzymatic Synthesis and Loosening Function for Cellulose Crystals | Biomacromolecules | ||||
北京佰司特科技有限責(zé)任公司
類器官串聯(lián)芯片培養(yǎng)系統(tǒng)—HUMIMIC;類器官灌流式培養(yǎng)和代謝監(jiān)測系統(tǒng)—IMOLA;
蛋白穩(wěn)定性分析儀—PSA-16;單分子穩(wěn)定性分析儀(磁鑷力譜測量儀)—HiMT;單分子質(zhì)量光度計—TwoMP;微流控擴(kuò)散測量儀—Fluidity One-M;
微納加工點(diǎn)印儀—NLP2000/DPN5000;臺式原子力顯微鏡—ACST-AFM;全自動半導(dǎo)體式細(xì)胞計數(shù)儀—SOL COUNT;農(nóng)藥殘留定量檢測儀—BST-100;
| 如果你對超高速視頻級原子力顯微鏡—HS-AFM感興趣,想了解更詳細(xì)的產(chǎn)品信息,填寫下表直接與廠家聯(lián)系: |



